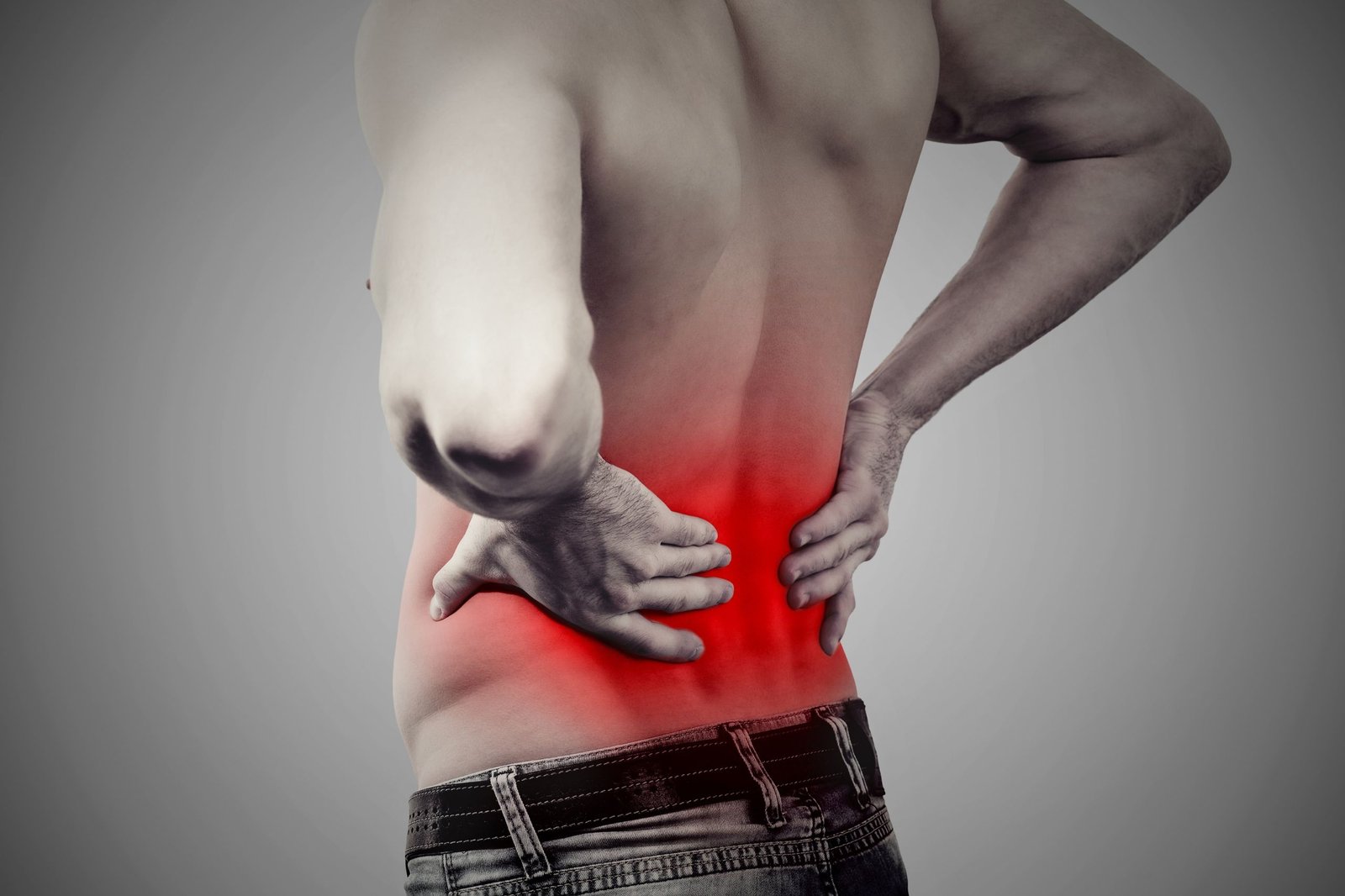
Brief Description
Acute lower back strain is a sudden injury typically caused by lifting heavy objects, improper posture, or sudden movements. It can result in sharp pain, stiffness, and limited mobility in the lower back. The pain may worsen with movement, making daily activities difficult. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) views this condition as an imbalance in Qi and blood circulation in the local area, often related to blocked meridians. Without proper treatment, the condition can worsen, leading to chronic pain.
Common Misconceptions
TCM Diagnosis
Typical Tongue
Typical Pulse
If the pain level is high, pulse can be fast and taut.
TCM Pathogenesis
Most acute lower back strains fall under the category of “tendon disorders” (筋病) in Traditional Chinese Medicine. These injuries often involve multiple meridians, leading to disruption in the flow of Qi and blood. This stagnation results in pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. The blockage in the meridians needs to be addressed to restore proper circulation and promote healing.
TCM Treatment
General Principle
Most acute lower back strains involve the Yang meridians, including the Taiyang, Shaoyang, Yangming meridians, and the Du meridian. Treatment focuses on identifying the affected meridians and using meridian-based diagnosis to restore proper flow of Qi and blood.
However, in some cases, the injury may involve the Yin meridians, particularly the Kidney meridian (Foot Shaoyin). Patients with such injuries often have a weak constitution and deficient Kidney Qi. In these cases, using conventional methods to unblock the meridians may be ineffective. Instead, a tonifying approach is necessary to achieve better treatment outcomes.
Unique Therapies We Apply
Treatment Plan
Precaution
Summary
Acute lower back strains are a common yet painful condition that can be effectively treated with Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). By addressing both the symptoms and underlying imbalances, TCM therapies help restore circulation, reduce pain, and promote faster recovery. Timely treatment is essential to prevent chronic issues, and avoiding prolonged rest and exposure to cold is key to maintaining proper circulation during the healing process.

The Traditional Chinese Medicine treatment approaches outlined above are derived from my clinical experience, and I acknowledge there may be areas not fully covered or that require further refinement over time.
This content is intended to provide a learning reference for professionals and enthusiasts in Traditional Chinese Medicine and to help patients gain a better understanding of their conditions and common misconceptions.
However, I must emphasize that this information does not constitute specific treatment guidance. All TCM treatments must be tailored to the individual through thorough diagnosis by a qualified practitioner. Non-professionals should not attempt self-treatment based on this information, as any treatment conducted without professional supervision may carry potential safety risks.
